The Coronavirus Economic Response Package (JobKeeper Payments) Amendment Bill 2020 was recently passed by Parliament to facilitate the extension of the JobKeeper Scheme to 28 March 2021. The Treasurer has subsequently released amended Rules for the Scheme, which were registered on 15 September 2020.
The below provides you a snapshot of the changes. There are a number of issues which require further clarification from the ATO which we have also highlighted.
JOBKEEPER 2.0 - SUMMARY
The main changes in JobKeeper 2.0 are:
-
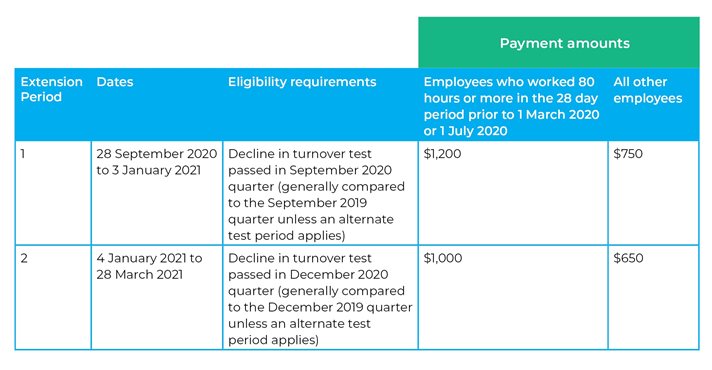
the need for employers to test their eligibility to receive JobKeeper payments for the period 28 September 2020 to 3 January 2021 and then again re-test their eligibility for the period 4 January 2021 to 28 March 2021;
-
the decline in turnover must now be calculated on actual turnover on a quarterly basis; and
-
the introduction of a two-tiered payment system for employees.
The following table summarises the payment amounts under JobKeeper 2.0:
HOW IS THE DECLINE IN TURNOVER TEST PASSED UNDER JOBKEEPER 2.0?
Depending on the turnover and type of entity, the following table summarises the turnover decline required for the relevant quarter, which has remained consistent with the original Rules:

Under the original decline in turnover test, you could use projections to determine the decline, and employers could choose the relevant month or quarter to be tested.
However, under JobKeeper 2.0, a new 'actual decline in turnover test' has been established. Employers can only test their eligibility based on their current GST turnover and can no longer use projections.
Importantly:
If a business satisfies the decline in turnover test in September 2020 but not in December 2020, it will be eligible for the 1st extension period but will not be eligible for the 2nd extension period.
The Rules state that the ATO has discretion to determine what is to be included in turnover for these purposes. It is expected that the ATO will determine that most supplies are made in the quarter in which the supplies are reported in the Business Activity Statement (i.e. on a GST attribution basis).
This suggests that the various options previously available under LCR 2020/1 may no longer be available for JobKeeper 2.0. We expect the ATO will soon clarify which of the options (if any) in LCR 2020/1 will be available for JobKeeper 2.0.
Alternative tests
As with the original Rules, the Commissioner has the ability to make alternative tests where the new actual decline in turnover test is not appropriate or cannot be met, for example, there is no comparison period. At this stage, the ATO has not issued any further information regarding alternative tests.
HOW IS THE PAYMENT RATE FOR ELIGIBLE EMPLOYEES DETERMINED?
The payment rate will be based on the number of hours an eligible employee worked during a 28 day period at the end of the most recent pay cycle ending before 1 March 2020 and 1 July 2020 (the relevant periods). Unlike wage condition, it does not matter when the actual payment is made to the employee.

If the employee worked 80 hours or more in either of the relevant periods, the employee is entitled to the higher rate outlined above, otherwise the lower rate applies.
When calculating the number of hours it is also necessary to include the number of hours the employee received paid leave (e.g. annual, long service, sick and carer leave) and paid public holidays.
Employers are required to check a 28 day period so you will need to pro-rata the number of hours worked if you use a monthly pay cycle.

Some points to note:
Remember to include employees as at 1 July 2020 under the previously announced amendments. See our previous article.
ELIGIBLE BUSINESS PARTICIPANTS
Eligible business participants are also subject to the same 80 hour test, and therefore must determine the hours they were actively engaged in the business. However, this test is only required to be done for the month of February 2020.
Individuals must be able to reasonably demonstrate the hours of active engagement required to claim the higher rate.
Care must be taken if the individual had other employment as it is likely they will not meet the 80 hour requirement above and therefore, would only be eligible for the lower rate.
Notifications also need to be made to the ATO in respect of sole trader eligible business participants, while other entities need to notify the relevant eligible business participant of the rate being applied.
FAIR WORK ACT CHANGES
Along with these changes, the Government also introduced changes to the Fair Work Act 2009 (FWA). Employers who continue to be eligible under JobKeeper 2.0 will receive the concessions previously afforded to them.
However, from 28 September onwards, no employers will be able to request employees to take annual leav.
Fair Work changes for employers who are not eligible for JobKeeper 2.0
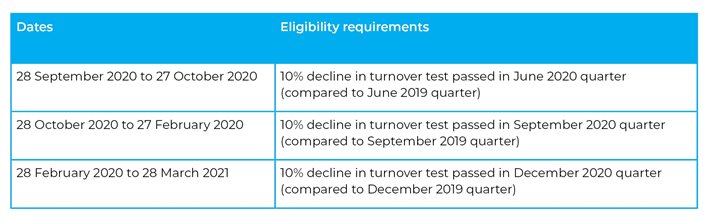
For employers who are previously eligible under JobKeeper 1.0 but do not meet the eligibility requirements for JobKeeper 2.0, there may be some concessions available if you continue to show a decline in turnover of 10% each quarter. Not to be confused with the 30% decline in turnover requirement for JobKeeper 2.0 eligibility this only allows concessions afforded under the FWA.
Employers (who are not small businesses) will need to get the decline in turnover certificate from an eligible financial service provider which includes tax agents. Small businesses employers (those with fewer than 15 employees) may make a statutory declaration instead of getting the certificate.
The employer will be able to rely on the FWA concessions during the following dates if the eligibility requirements are met during the relevant quarter and a certificate or declaration has been obtained:
Eligible employers who meet the requirements above will be able to:
-
Give employees for whom the employer previously received a JobKeeper payment a:
-
JobKeeper enabling stand down direction (to no less than 60% of the employee’s ordinary hours as at 1 March 2020, and that does not require the employee to work less than two consecutive hours in a day);
-
JobKeeper enabling direction regarding duties of work; or
-
JobKeeper enabling direction regarding location of work; and
-
Request employees for whom the employer previously received a JobKeeper payment agree to perform their duties on different days or at different times (as long as the agreement does not require the employee to work less than two consecutive hours in a day).
For more information in relation to the changes to the FWA, refer to the FWA website.
NEXT STEPS
Employers do not need to register for the extension if they are already in receipt of JobKeeper payments under the existing scheme.
To ensure eligibility for JobKeeper 2.0, employers should:
-
Get accounting records in order and ensure these are up to date by early October as the eligibility is based on actual results for the quarter ending 30 September 2020.
-
Keep the accounting records up to date to ensure eligibility for the second quarter which is based on actual results for the quarter ending 31 December 2020.
-
Compile payroll records for all eligible employees and check the number of hours they worked on average during the relevant periods prior to 1 March 2020 and 1 July 2020.
-
Ensure the minimum wage condition is met based on the higher or lower rate (as appropriate).
If you require any assistance in understanding these rules, please contact your local Moore Australia advisor.